

The study of the joint evolutions of these twin universes corresponds
to the two following papers :
- J.P.Petit & P.Midy : Matter ghost-matter astrophysics.3 : The
radiative era :The problem of the "origin" of the universe. The problem of
the homogeneity of the early universe. Geometrical Physics A , 6 , 1998.
- J.P.Petit & P.Midy : Matter ghost-matter astrophysics. 1.The geometrical
framework. The matter era and the newtonian approximation. Geometrical Physics
A , 4 , 1998.
...We
can define length scales R and
R*. We study the evolution with
respect to the time t of the first universe, supposed to be ours ( but, possibly
: t* = - t ). In a word : we decide to describe the evolutions of the two
universe with the same time-marker t.
...During the radiative era we assume R(t) varies like R*(t). We assume the two universes to be closely coupled. Then, when radiative era ends in both folds, the matter dominated era starts. Let us first study this second period
...If
the two densities r
and
r*
are assumed to be
equal ( in matter dominated era the pressures p and p* are negligible, like
in the classical Friedmann's models ), the tensors
T and
T* are
equal. Then the field equations reduce to .
(142)
whose common solution is
(143)
and corresponds to a linear expansion
in the two universes. We show in the mentioned paper that such expansion is
unstable. One of the two universes starts to expand faster than the other,
which decelerates. See Geometrical Physics A , 4 , 1998, section
2.
(144)
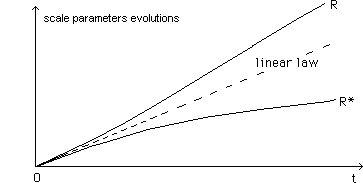
...The
two laws R(t) and
R*(t) depart from their
common initial linear evolution. We assume R(t) corresponds to our own universe.
In figure (145) the standard model, with a null cosmological constant.
(145)
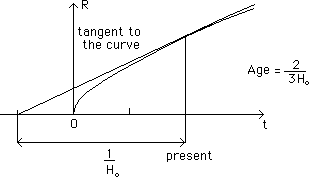
...In 1994 the Journal Nature evoked a serious problem about the age of the universe, after measurements performed by the Hubble space telescope on distant galaxies, where the satellite discovered cepheids.
...It appeared that the distances of these galaxies had been overestimated. The corresponding new valueof the Hubble's constant value, enlarged, shortened the age of the universe to 8-9 billions years.
...Until 1994 the age of the oldest stars of our galaxy, located in globular clusters, were estimated to be to some 15-20 billions years old.
...After the measurements in 1993-1994 by Hubble telescope's, the universe became younger than its own stars !
...Four years after, the situation looks not quite so critical, for two reasons.
- From Hipparcos satellite measurements, the calibration of cepheids was modified.
- The theoreticians made large
efforts to shorten the age of the oldest stars of globular clusters.
But this problem isn't closed yet.
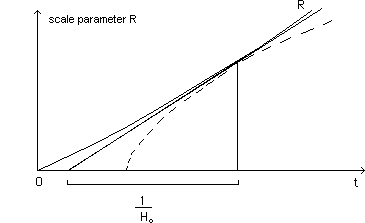
...Next
figure shows how the Twing bang model enlarges systematically the age of our
universe, with respect to the Standard Model (dotted line) for a given value
of the Huuble's constant Ho.
(146)
...In figure 144 we see how the ghost matter propels our matter "forwards", accelerating our expansion process. Conversely we can slow down the expansion of the ghost universe (described with respect to our time t, of course). So that the ghost universe acts like a "cosmological constant". Classically one considers that the cosmological constant corresponds to the repulsive power of vacuum. In this model the ghost universe owns a "repulsive power", accelerating our expansion.
![]()